Documents
Skyve uses the term document to indicate the business-focused nature of application objects.
In an office environment, users interact with paper or electronic documents and are familiar with a documents being self-contained artefacts with different types of content, often created using a template.
Skyve documents are the core components of Skyve applications. All user application data is contained within documents.

Within the application file structure, each document is assigned a package.
The document package includes declarations of actions, reports, views and the associated Bizlet file. The Bizlet file contains document-specific behaviours including overrides of default action behaviours and document bean lifecycle events (e.g. newInstance, preSave, etc.).
Other java class files can be located within the document package if required.
Document.xml
Inside the document package, the document.xml file defines aspects of a document, including:
- document metadata (name, description, aliases),
- bizKey (business key),
- attributes (fields & references),
- conditions,
- constraints, and
- documentation (doc).
Documents may be persistent (persisted in a database) or transient (memory only).
If a document exists as a child of another document and should not be orphaned, the document.xml will nominate the parent document.

Document.xml sections
Metadata
Each document.xml includes the following metadata:
| Metadata | Description |
|---|---|
| name | The unique name of the document within the module context. This name defines the Java class name and how the document is referred to within developer code, e.g. ‘Contact’. Because documents are implemented as Java interface classes, document names are Titlecase. |
| persistentName | The name of the database table in which instances of the document will be persisted as tuples. By convention, persistentNames are prefixed for each module, e.g. ‘ADM_Contact’. |
| singularAlias | The name of a document instance as used by users of the application, e.g. ‘Weekly Timesheet’. |
| pluralAlias | The plural form of the singularAlias, so that a collection of document instances can be referred to in a grammatically correct way, e.g. ‘Timesheets’. |
| parentDocument | The name of the document which is the parent of this document (if applicable), e.g. if the document is TimesheetLine, the value of parentDocument would be Timesheet. |
Document.xml sections
Persistent documents
If the document includes a persistent declaration, instances of the document will be persisted in the primary data store (database).
An example persistent declaration is:
<persistent name="ADM_Contact"/>
In this case the combination of name, catalog and schema describe where rows corresponding to the document instances will be stored in the primary data store. Typically catalog and schema if the tables are to be in the primary catalog or schema of the primary data store (as per the settings in the deployed .json settings file), however these can be specified here if the table is located in another area.
Persistent strategy and inheritance
Skyve supports inheritance between documents, to maximise re-use, and improve quality.
If you have a number of documents that have a subset of common attributes, you can declare an abstract document with the common attributes, and then other documents that extend this, inheriting behaviours and taking advantage of reusable view components.
See more details at Inheritance
Cache
Skyve 3.0.0 introduced support for in-memory caching via the metadata and for developers in code. This adds a write-through cache option per document using an in-memory cache that sits between Hibernate and Skyve’s persistence layer. If declared, the read and write operations are to/from the cache. Skyve handles keeping Hibernate and the persistent datastore in sync.
<persistent name="ADM_Contact">
<cache>reference</cache>
</persistent>
Declaring a cache for a persistent document has the effect of increasing the memory load on the server but decreasing the load on the database, so for example, in servers where there is a H2 database co-located it will have minimal noticeable performance impact. However if you are accessing a database across a network and you have an expensive document to read from/write to, this could have quite a noticeable impact on application performance. For developers, the CacheUtil utility class can be invoked by developers and Skyve will handle the management of the cache. A getJCache() and getEHCache() method can be used depending on the type of cache required.
Hibernate caching in Skyve works in tandem with database caching mechanisms. The hibernate second level cache stores an internal representation of the object approximating the tuple rather than the domain object - no non-persistent representation foreign keys, un-related object etc. These are inflated to the first level cache (as domain objects). There is one second level cache and multiple first level caches per Skyve conversation.
If items are in the cache and a DocumentQuery is used to retrieve items, the database is interrogated to get the results of filtering etc, however the objects are hydrated from the cache rather that from the database.
The cache name refers to a name that has been declared in the deployed .json properties file within the hibernate properties stanza as follows:
The hibernate stanza needs a new cache section to define the default Skyve caches, and is where any per-project custom cache settings are to be defined:
prettySql: false,
caches: {
"eternal": {
// Max conversations allowed in heap memory before being moved off-heap or to disk
heapSizeEntries: 10,
// Max off-heap memory size - 0 indicates no usage
offHeapSizeMB: 0,
expiryPolicy: "eternal" // "timeToLive" or "timeToIdle"
},
"reference": {
// Max conversations allowed in heap memory before being moved off-heap or to disk
heapSizeEntries: 1000,
// Max off-heap memory size - 0 indicates no usage
offHeapSizeMB: 0,
expiryPolicy: "timeToIdle", // "timeToLive" or "eternal"
// Number of minutes to wait until expiring a hibernate object from the cache
expiryTimeMinutes: 10
}
}
The eternal and reference examples are provided by default, however are merely examples and caches can be declared here as required.
Using the above examples, if the Contact document was declared using the eternal cache, then the most recent 10 Contacts loaded from the database will remain in the cache while the application runs. If another Contact is loaded, then the oldest cache item is removed and the new item added to the cache and so on.
Similarly, for the reference example above, the cache will contain up to 1000 Contacts but in this case each item will only remain in the cache for 10 minutes before being expunged.
SingletonCachedBizlet
For documents where there is only one instance per datastore, user, datagroup or customer, you can implement the SingletonCacheBizlet class rather than use the persistent declaration for the document.
This approach is described in detail at Singleton Documents
Note that whereas Hibernate caching is for caching a result set or multiple records, the singleton just holds onto a single object in memory. This would cause memory pressure if you tried to use this strategy for large result sets.
bizKey
To enable the application to display references simply, each document
must define a business key (bizKey) definition (similar to a Java
toString() method for the document). The bizKey is the default
representation of the entire document instance.
For example, a contact might have a bizKey of {name} whereas a
timesheet might have a bizKey composed of {user} and {weekending date}.
By mandating that every document has a bizKey there is always a default representation available to the Skyve platform.
The bizKey declaration can contain a binding expression, or developer code (e.g. a call to a method in a Bizlet class).
An example bizKey expression for a person Contact document might be:
<bizKey expression="{name} ({mobile})"/>
An example bizKey referencing a coded method might be:
<bizKey>
<![CDATA[
return modules.admin.Contact.ContactBizlet.myBizKey(this);
]]>
</bizKey>
In this example, method myBizKey() is a method created by the developer in the ContactBizlet class.
When the class is generated, the code included in the bizKey section
is placed verbatim in the generated implementation (Impl) class in the
myBizKey() method. This means that the bizKey code must be compilable
within the context of that class.
If the bizKey section contains invalid or uncompilable code, the domain Impl class will not compile.
Attributes
Documents may have any number of attributes which can be scalar (simple value) or complex (references to other documents etc).
The order in which attributes are defined in the document.xml implies a default ordering for lists and views.
By default, all attributes are persisted and not required, unless otherwise declared by the developer.
Attributes must have, as minimum, a name (the logical name as used by the developer) and displayName (the business name as used by application users - this will usually be the label of the input widget in a view).
Attribute declarations may include a defaultWidget declaration which provides the platform with default representation information. If no defaultWidget is supplied, Skyve will infer a widget from the attribute’s type. The developer can also override a defaultWidget by specifying a widget in a view definition.
If an attribute includes a description, this will be rendered as tool-tip help button in the detail view. The description can contain simple markup as it will be rendered as HTML.
Attribute usage
The usage attribute in Skyve is used to differentiate between Domain Model and View Model attributes within a document’s metadata declaration. This provides a structured way to indicate whether an attribute is intended for backend data persistence, user interface representation, or both.
Usage Values:
domain: The attribute is intended solely for the domain model. It may be included in persistence or business logic but may not be relevant for user interaction in the UI.view: The attribute is used only in the view model, meaning it is relevant for UI rendering but probably not stored in the database.both(default if not specified): The attribute is used for both domain and view models, meaning it probably persisted as well as being displayed in the UI.
Effects of usage:
- Data Builders & filtering:
- The
DataBuilder class can filter attributes when generating test data, ensuring only domain attributes are used in test builds.
- The
AbstractDomainTestbehavior:- Skyve’s
AbstractDomainTestlogic ensures that test validation does not mistakenly include view-only attributes in domain-level operations.
- Skyve’s
- Auditing defaults:
- If an attribute is set to
viewand does not have an explicit audit configuration, it defaults to not audited, ensuring auditing remains relevant to persisted data.
- If an attribute is set to
Example:
<text name="displayOnlyField" persistence="false" usage="view">
<displayName>Display Only</displayName>
<description>This field is used only for UI rendering and is not persisted.</description>
</text>
<text name="persistedField" usage="domain">
<displayName>Stored Field</displayName>
<description>This field is stored in the database but is not intended for UI display.</description>
</text>
Attribute sensitivity
When adding attributes to a document, a developer should consider the sensitivity level of the data that will be used. The sensitivity level is used during skyve’s backup feature to obfuscate certain data based on how sensitive it is. This is a security feature allowing a business to make a backup of their data to share with others while ensuring that whoever receives the backup sees only that which they have access to.
There are six sensitivity levels to choose from, highlighted below in ascending order of data sensitivity. This hierarchy ensures that as you progress from “None” to “Secret”, the data becomes increasingly sensitive, necessitating stricter controls and more robust obfuscation when shared during backups.
- None – This data is regarded as non-sensitive and can be shared freely with any party without restrictions. It poses no risk to the business or individuals if it becomes public.
- Internal – Information intended for use within the organisation. It is not meant to be shared externally, but it does not contain critical or highly sensitive data. Sharing it outside the organisation could potentially cause minor issues.
- Confidential – This data is sensitive and should only be shared with trusted individuals or departments. Unauthorized access could harm the organisation’s operations or reputation. It is protected, and access is generally restricted to specific roles.
- Restricted – Data that is sensitive and closely controlled. Access is typically limited to a small group of authorised individuals within the organisation. Improper sharing of this data could lead to significant legal, financial, or operational consequences.
- Personal – This pertains to personally identifiable information (PII) like names, addresses, or any data that may be associated with an individual. Unauthorised disclosure of personal information can give rise to privacy breaches, legal repercussions, and a loss of trust.
- Secret – The most sensitive level of information, where unauthorised access could lead to severe consequences, such as financial loss, reputational damage, or exposure of critical business or security-related information. Strict protocols are necessary to manage, store, and share this data securely.
Obfuscation strategies
Skyve attempts to ensure that sensitive data is obfuscated while retaining enough information for testing or debugging purposes. Different attribute types are obfuscated in different ways to ensure that the data is not easily readable while still being usable in a backup context. Obfuscation is not intended to be reversible, and the original data should not be recoverable from the obfuscated data.
- Text Attributes (
text,markup,memo,id):- Text attributes are redacted by masking the middle part of the string with asterisks (
*). - For email addresses, the part before and after the
@symbol is separately redacted. - The number of visible characters at the start and end of the string depends on its length.
Example:
Input: "example@example.com" Output: "ex****@ex****" - Text attributes are redacted by masking the middle part of the string with asterisks (
- Numeric Attributes (
integer,longInteger,decimal2,decimal5,decimal10):- Numeric attributes are rounded to the nearest multiple of 10.
- This ensures that the original value is obfuscated while retaining a general sense of scale.
Example:
Input: 123 Output: 120 - Date Attributes (
date,dateTime,timestamp):- Dates are rounded to the first day of the month.
- Timestamps are further rounded to midnight on the first day of the month.
Example:
Input: 2023-10-15 Output: 2023-10-01 - Time Attributes (
time):- Time attributes are rounded to the nearest hour, with minutes and seconds set to zero.
Example:
Input: 14:37:45 Output: 14:00:00 - Geometry Attributes (
geometry):- Geometric coordinates (latitude and longitude) are rounded to the nearest whole number.
- This reduces precision while maintaining approximate location information.
Example:
Input: Point(123.456, 78.910) Output: Point(123, 79) - Content and Image Attributes (
content,image):- These attributes are nullified to completely remove sensitive data.
Example:
Input: Binary content Output: null
Attribute types
Developers should note that database specific implementations of each type are defined by Hibernate mapping settings and not by the Skyve specification.
The following attribute types are available:
| Attribute type | Description | Default widget | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| association | A reference to another document. Associations may be either an aggregation or composition and must include the name of the document which is the subject of the association. Associations may optionally include queryName - the name of a metadata query defined in the module.xml which provides eligible document instances. Associations of type composition will cascade delete. |
lookup | 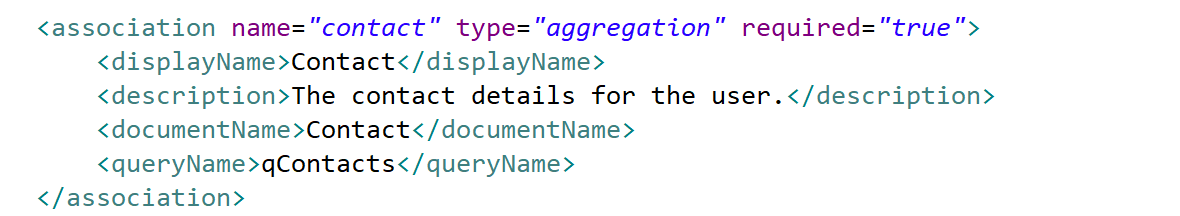 In this example, the document has a reference to the Contact document called Contact. If the association above was type composition (rather than aggregation), deletion of the document would cascade and delete referenced Contacts. Note that specifying a queryName is optional. If no queryName is specified, Skyve will supply the default or generic inferred query for the associated document. |
| boolean | True or False If a boolean attribute is not marked as required, the value may also be null. |
checkBox | 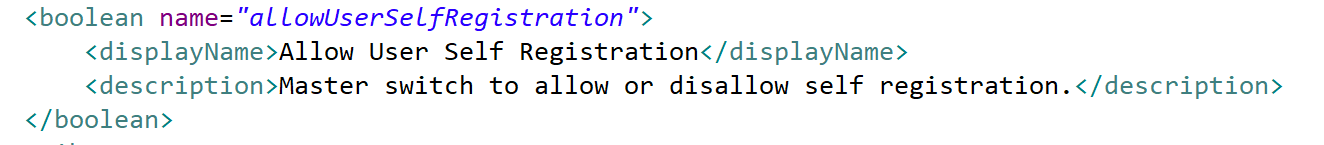 In this example, the attribute is not required. Non-requiredness means that null is a valid value for the attribute. |
| collection | An orderable collection of references to another document. Collections must specify the documentName - the name of the document which is the subject of the collection. Collections may be either child, aggregation or composition type. Child collections belong to the document and cascade deletion will occur. Members of child collections have a parent reference automatically created and assigned. By default, interactions with child members will occur in modal windows and within the same transaction as interactions with the parent. Optionally, collections may declare their usage (“domain”, “view” or “both”) - this is a hint to developers about how the collection is used and for example can be used by developers to control whether collections are filled by Factory classes or in other generic code. Collections must have a minCardinality (which can be 0) and may optionally have a maxCardinality. Collections may be ordered, either implicitly by the user (drag and drop within a grid) or specifically by the developer (using the order by clause). Collections may specify a uniqueness constraint within the context of the parent’s collection (rather than within the customer’s scope). Aggregation and composition collections may specify a queryName unless the document’s default query is to be used to define eligible document instances. |
dataGrid (child, composition) OR dataGrid with a row containing a lookup (aggregation) |
 In this example, the document has a collection of children called Interactions. Since minCardinality is 0, the document will be valid even if no children exist. The collection will be automatically reordered as defined by the ordering clause (interactionDate, then interactionTime, then interactionType) whenever the bean is saved. All interactions will have a reference to the document called parent. If the document is deleted, all children will also be deleted.  In this example, the collection is ordered, meaning that the user can re-order the collection by drag-drop in the view. The ordering performed by the user will be preserved when the bean is saved. This example includes a uniqueness constraint applied within the context of the collection to prevent the same ContactCategory being added twice to the same collection. Because the collection is of type aggregation (rather than composition) deleting the document will not cause cascade delete of the ContactCategory members of the collection. |
| colour | A colour. | colourPicker | 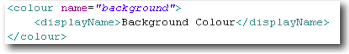 In this example no shortDescripiton is declared and as such no tool-tip help icon will be displayed next to widgets bound to this attribute. |
| content | Complex objects like movies, sound, word processing documents, spreadsheets, etc. Content objects are automatically indexed by the textual indexer. |
contentLink |  |
| date | A calendar date (year, month, day). By default, Skyve will provide a calendar widget for selection, but the date can be modified as text. Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField | 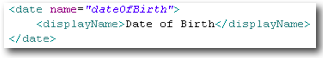 |
| dateTime | Date with time (hours, minutes). By default, Skyve will provide a calendar with time widget for selection, but the date and time can be modified as text. Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField | 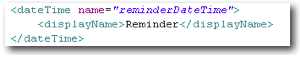 |
| decimal2 | Decimal number rounded to 2 decimal places, commonly used for currency and percentages. Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField | 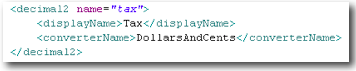 In this example, the converter DollarsAndCents is automatically applied wherever this attribute is displayed. |
| decimal5 | Decimal number rounded to 5 decimal places. Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField | 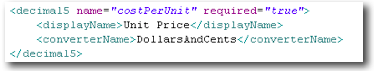 |
| decimal10 | Decimal number rounded to 10 decimal places. Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField |  |
| enum | A declared value set of static values for user selection (see full description below) | combo |  In this example, an enumeration will, by default, be represented as a simple combo box, with the four nominated descriptions in the combo list. Because descriptions have been supplied, the codes will never be seen by the user, but will be persisted in the database. Because name attributes have not been supplied for the values, the domain class for the document will include a Java enumeration with elements named as valid Java identifiers based on the description values, as shown:  |
| geometry | Used for storing location and geographical features in the Skyve platform (using a “flat-earth” cartesian approach - i.e. a non-geodetic feature on a 2-dimensional plane). | geometry |  |
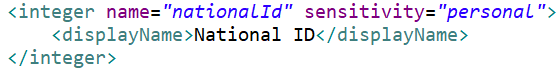
| integer | An integer between the values of 2\^31-1 and -2\^31-1. Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField | 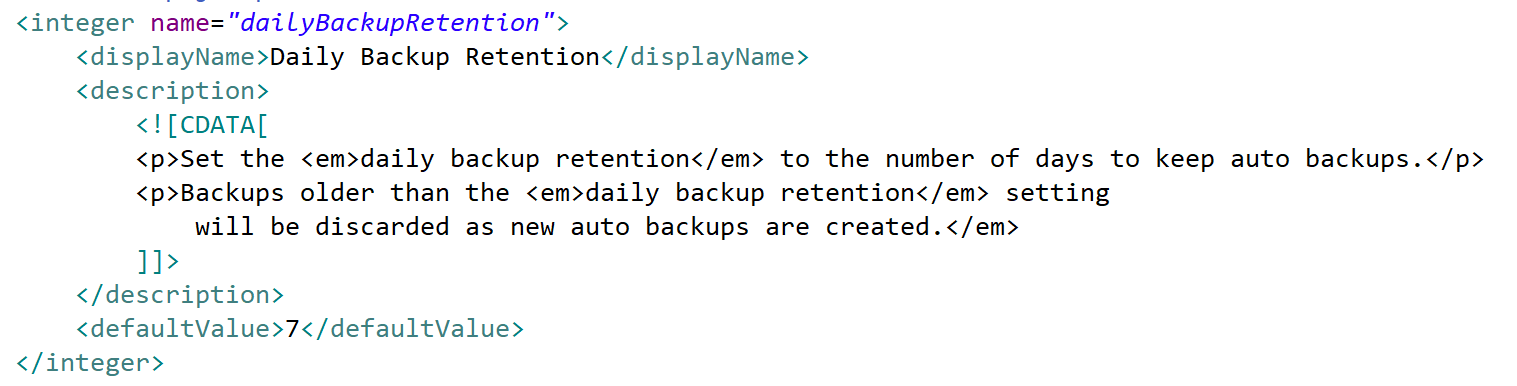 In this example the attribute has a description containing markup to provide expansive formatted tool-tip help. The defaultValue setting in this case will yield a default value in the generated domain class as follows:  |
| longInteger | A large integer. Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. In this example, the attribute declares that a database index is to be maintained. |
textField | 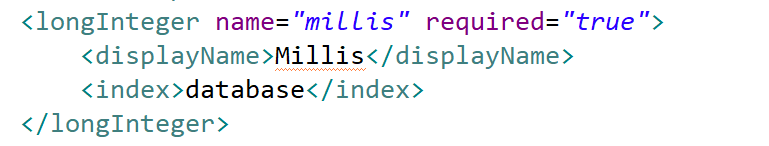 |
| markup | Text with embedded markup tags. Markup is the same as a memo where the textual indexer knows it will be HTML and will ignore HTML tags. |
richText | 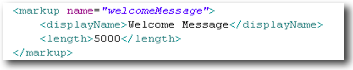 In this example the length will be applied and the user will be prevented from entering more than 5000 characters in the client (on keyPress event). If the developer makes an error in code and attempts to set a longer value, an exception will be thrown when the code attempts to persist the bean. The markup tags are included in the character count (but won’t be indexed). |
| memo | Generic text values which are intended for large or formatted text values. Memo attributes are automatically indexed for textual searching. As indexes are created by default by Skyve for memo attributes, in this example, the attribute declares that no index is created. |
textArea | 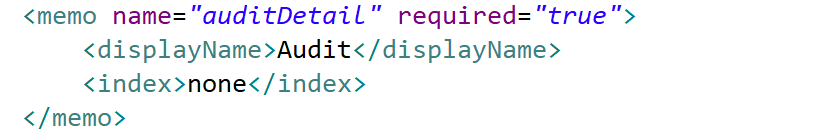 |
| text | Generic text values. Text attributes can be marked as indexed either for textual searching, or as a database index. Text attributes may specify a value domain either constant, variant or dynamic - loosely typed value lists generated by methods in the document Bizlet. |
textField OR combo if a domain is specified |
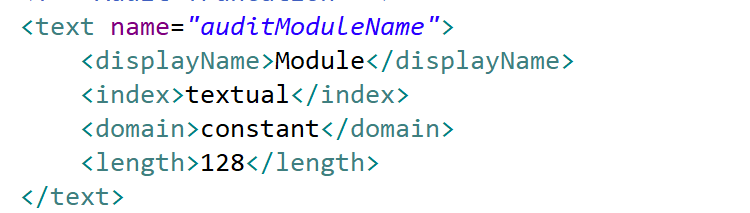 In this example the method attribute is textually indexed. Normally constant domains are implemented as enum type attributes, but in this case, the developer will be responsible for generating the domain value set (by overriding the getConstantDomainValues() in the Bizlet. By default the attribute will be displayed as a simple combo with the generated value set included in the combo list to constrain users to that value set.If the developer sets a value which is not returned by the getConstantDomainValues() method (i.e. not in the domain value set), the bean validation will throw an exception to prevent the value from being persisted. |
| time | Time (hours, minutes, seconds). Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField |  |
| timestamp | Date with time (hours, minutes, seconds). Note that if a converter has been declared, the representation within the textField component will reflect that conversion. |
textField | 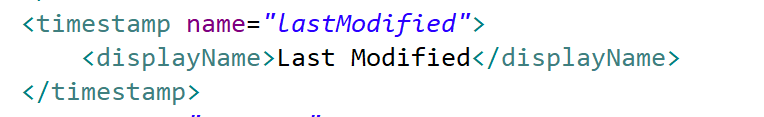 |
| inverseOne | See Inverses | ||
| inverseMany | See Inverses |
Document attribute types
Enumerations
Declaring enum
An enumeration is a text field which is constrained to be one of a set of values, and can either declare values or refer to another attribute value set.
If enumerations are not marked required, they may be set to null.
| Value attribute | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
code |
the value stored when this value is selected & the value stored in the persistence mechanism | required |
description |
how the value is displayed to the user - if the description is not explicitly declared it will be inferred from the code |
optional |
name |
how the value is referred to in developer code and metadata - if the name is not explicitly declared it will be inferred from description |
optional |
name must be compilable as a Java identifier.
Skyve will infer the name if it is not explicitly declared and if inference from the code or description does not lead to a satisfactory Java identifier, compile errors may result from the domain generation. In this case, declare a preferred name explicitly.
When declaring an enumeration note that the defaultValue must correspond to the name of the value.
<enum name="loadAction">
<displayName>Action</displayName>
<defaultValue>lookupLike</defaultValue>
<values>
<value code="set" name="setValue" description="Always set this value"/>
<value code="equals" name="lookupEquals" description="Look for exact match"/>
<value code="like" name="lookupLike" description="Look for like match"/>
<value code="contains" name="lookupContains" description="Look for matches containing this value"/>
<value code="confirm" name="confirmValue" description="Fail if this value doesn't match"/>
</values>
</enum>
In the above example, when the first value is selected from by the user, the code set will be stored (in the persistence mechanism), while the description Always set this value will be presented to the user.
To determine which value has been set can take advantage of the switch operator using the attribute getter as follows:
switch(getLoadAction()) {
case confirmValue:
//user code
break;
case lookupContains:
//user code
break;
case lookupEquals:
//user code
break;
case lookupLike:
//user code
break;
case setValue:
//user code
break;
default:
break;
}
To declare additional attributes using the same value set, use the attributeRef option in the enum declaration. If the value set is declared on an attribute in a different document, use the attributeRef and documentRef to specify the source. If the source is in a different module, use the attributeRef and moduleRef and documentRef.
<enum name="otherAction" attributeRef="loadAction">
<displayName>Action</displayName>
</enum>
When the domain is generated, the enum will result as follows:
/**
* Action
**/
@XmlEnum
public static enum LoadAction implements Enumeration {
setValue("set", "Always set this value"),
lookupEquals("equals", "Look for exact match"),
lookupLike("like", "Look for like match"),
lookupContains("contains", "Look for matches containing this value"),
confirmValue("confirm", "Fail if this value doesn't match");
private String code;
private String description;
/** @hidden */
private DomainValue domainValue;
/** @hidden */
private static List<DomainValue> domainValues;
private LoadAction(String code, String description) {
this.code = code;
this.description = description;
this.domainValue = new DomainValue(code, description);
}
@Override
public String toCode() {
return code;
}
@Override
public String toDescription() {
return description;
}
@Override
public DomainValue toDomainValue() {
return domainValue;
}
public static LoadAction fromCode(String code) {
LoadAction result = null;
for (LoadAction value : values()) {
if (value.code.equals(code)) {
result = value;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public static LoadAction fromDescription(String description) {
LoadAction result = null;
for (LoadAction value : values()) {
if (value.description.equals(description)) {
result = value;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
public static List<DomainValue> toDomainValues() {
if (domainValues == null) {
LoadAction[] values = values();
domainValues = new ArrayList<>(values.length);
for (LoadAction value : values) {
domainValues.add(value.domainValue);
}
}
return domainValues;
}
}
Note that to set the value of the enum attribute from a String, use the fromCode or fromDescription as is appropriate.
The Binder.formatMessage() method will return the declared (or inferred) description, as follows (using the example attribute declaration above):
String output = Binder.formatMessage(CORE.getCustomer(), "You have selected the action `{loadAction}`.", bean);
Enum with domain
You can conditionally restrict the list of enum values available to the user by declaring an enum attribute with a domain. This means that from the full list of values declared within the document (being generated into a proper Java enum for compile time checks), you can restrict the values available to the user at run time to those that are relevant.
By declaring a domain, the values available to the user will be constrained to those resulting from the Bizlet domain method.
For example, the admin Data Maintenance function provides a number of restore types to handle restoring a database from a previous or later version of the same application:
<!-- Restore parameters -->
<enum name="restorePreProcess">
<displayName>Pre-Process</displayName>
<domain>constant</domain>
<values>
<value code="noProcessing" description="No Processing" />
<value code="dropUsingMetadataAndCreateUsingBackup" description="Drop tables using metadata & recreate tables from backup create.sql" />
<value code="dropUsingBackupAndCreateUsingBackup" description="Drop tables using backup drop.sql & recreate tables from backup create.sql" />
<value code="dropUsingMetadataAndCreateUsingMetadata" description="Drop tables using metadata & recreate tables from metadata" />
<value code="dropUsingBackupAndCreateUsingMetadata" description="Drop tables using backup drop.sql & recreate tables from metadata" />
<value code="createUsingBackup" description="Create tables from backup" />
<value code="createUsingMetadata" description="Create tables from metadata" />
<value code="deleteData" description="Delete existing table data using metadata" />
</values>
</enum>
In this case, the document declares all valid enum values, but also declares a constant domain. In this case, the values available to the user will be limited by the getConstantDomainValues() Bizlet method as follows:
@Override
public List<DomainValue> getConstantDomainValues(String attributeName) throws Exception {
List<DomainValue> result = null;
...
else if(DataMaintenance.restorePreProcessPropertyName.equals(attributeName)){
result = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(RestorePreProcess.noProcessing.toDomainValue());
if(UtilImpl.CUSTOMER!=null){
result.add(RestorePreProcess.dropTablesUsingMetadataRecreateTablesFromBackupCreatesql.toDomainValue());
result.add(RestorePreProcess.dropTablesUsingBackupDropsqlRecreateTablesFromBackupCreatesql.toDomainValue());
result.add(RestorePreProcess.dropTablesUsingMetadataRecreateTablesFromMetadata.toDomainValue());
result.add(RestorePreProcess.dropTablesUsingBackupDropsqlRecreateTablesFromMetadata.toDomainValue());
result.add(RestorePreProcess.createTablesFromBackup.toDomainValue());
result.add(RestorePreProcess.createTablesFromMetadata.toDomainValue());
}
result.add(RestorePreProcess.deleteExistingTableDataUsingMetadata.toDomainValue());
}
}
Inverses
The inverseOne and inverseMany attributes are used in conjunction with association and collection attributes to define the inverse relationship between documents. These attributes provide bidirectional navigation between related documents, without requiring explicit foreign key references in both directions. These attributes are non-persistent and will not create a column in the defined document’s table.
inverseOne
The inverseOne attribute is used like an association to define the inverse reference to an association on the referenced document. This is used when only one record on the inverse side relates to a single record on the target side.
Effects of inverseOne:
- It establishes a bidirectional relationship where the target document has an association containing the referring document (one to one).
- This allows Skyve to infer the relationship without requiring an explicit foreign key reference on both sides.
- The association must be declared on the referenced document.
- The inverseOne attribute can be included in views as a binding, or in module queries as a column.
<!-- Contact.xml document -->
<inverseOne name="customer">
<displayName>Customer</displayName>
<documentName>Customer</documentName>
<referenceName>primaryContact</referenceName>
</inverseOne>
In this example:
- The
Customerdocument defines an association to aContactnamedprimaryContactthat contains a Contact instance. - The
Contactdocument has an inverse relationship to aCustomer. - This allows Skyve to resolve the inverse relationship without additional metadata.
inverseMany
The inverseMany attribute is used like a collection to define the inverse reference to an association on the target document. This is used when many records on the inverse side relate to a single record on the target side.
Effects of inverseMany:
- It allows Skyve to resolve the inverse reference dynamically without requiring an explicit foreign key.
- When an instance of the target document is modified, Skyve ensures that the reference is properly updated on both sides of the relationship.
- This is useful when the parent document does not explicitly store a reference to a child, but needs to navigate back to it.
<!-- Customer.xml -->
<inverseMany name="contacts">
<displayName>Contacts</displayName>
<documentName>Contact</documentName>
<referenceName>customer</referenceName>
</inverseMany>
In this example:
- The
Contactdocument has an association to a Customer namedcustomer. - Skyve will automatically resolve the relationship, allowing a
Customerto retrieve itscontactswithout an explicit database reference. This can be used as if a collection ofContactinstances were stored in theCustomerdocument.
Cascade
The cascade attribute can be specified to cascade the save and delete operations to the inverse document. This is useful when the inverse document is a composition and should be deleted when the parent document is deleted, or changes made in an edit view should flow across the inverse to the persistent attribute.
Conditions
Document conditions are code snippets which return a Java boolean value,
and which can be used by view declarations.
By restricting client-side view conditions to server-side compiled code, rather than client-side Javascript (or other client script), the risks of developer bugs is significantly reduced. Only the result of the condition is passed to the client, so the chance of an invalid or unintended result is minimised. This also means that client interactions can have access to the results of the full breadth of the server-side code base, utilities and libraries, while all code is maintained in one central location. The additional benefit is that all application code is in one language.
<condition name="personType">
<expression>
<![CDATA[ContactType.person.equals(getContactType())]]>
</expression>
</condition>
Although available to client-side views, conditions can take advantage of strongly typed compiled code or validated expressions.
Condition declaration
Conditions become methods of the generated document classes. The code within the condition declaration is placed verbatim in the method, allowing condition methods to be used in developer server-side code (e.g. Bizlet or Extension code).
For each condition declaration, Skyve generates pairs of condition methods (both positive and negative methods are generated).
@Override
public boolean isPersonType() {
return (ContactType.person.equals(getContactType()));
}
@Override
public boolean isNotPersonType() {
return (ContactType.person.equals(getContactType()));
}
Generated condition method pairs.
Expression conditions
In addition to declaring conditions using Java, conditions can also make use of Skyve expressions for evaluation which can be used to return a boolean. For example, to write a simple condition checking if a boolean attribute is true:
<condition name="showExistingGroups">
<expression>
{el:bean.groupsExist}
</expression>
</condition>
instead of the alternate Java logic which would be defined as Boolean.TRUE.equals(groupsExist).
Constraints
Uniqueness constraints can be defined within the document.xml.
Constraints are checked using row locking (where available, e.g. using the select for update syntax or the update hint in MS SQL Server).
Constraints can combine any number of attribute references (refs) and are declared against a scope (either user, datagroup, customer or global).
<uniqueConstraints>
<constraint scope="customer" name="UniqueSystemCommunication"
description="Ensure no duplication of communication templates">
<message>A communication for {description} already exists.</message>
<fieldReferences>
<ref>description</ref>
</fieldReferences>
</constraint>
</uniqueConstraints>
The message is displayed to the user when the constraint is violated, and may contain bindings.
In the above example, the constraint will ensure uniqueness of the system communications per customer.
Documentation
The document.xml includes a <documentation> tag to allow document
specific documentation to be included with the document definition.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<document name="Subscription" xmlns="http://www.skyve.org/xml/document" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.skyve.org/xml/document ../../../schemas/document.xsd"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<documentation>
<![CDATA[
A Subscription models the receiver's preference about how
they wish to receive the communication type (or not).
If the subscription is declined, the format type is not required.
If the format type is supplied, then the communication
is only declined for that format.
If the subscription is not declined, the format type is required,
as this specifies the format preference for the communication.
If the subscription is not declined and has no formatType,
the subscription can be deleted as it holds no value.
Subscriptions are user-scoped - The assumption is that it is up to
the user whether they wish to accept or decline receiving
communications and in what manner they are delivered.
]]>
</documentation>
<persistent name="ADM_Subscription" />
documentation tag for a document
Overriding documents
Documents may be overridden for customers, to allow customised variants of the document definition including:
- attribute names and descriptions,
- attribute types and sizes,
- attribute converters,
- default widgets,
- conditional logic,
- relationships and constraint particulars, and
- views, actions, reports and Bizlet methods.
To override a document, view, action, report or Bizlet method, place the overriding artefact into the customer package, mirroring the folder structure of the originating artefact.
When overriding Bizlet methods, only the methods being overridden should occur in the overriding Bizlet class (placed in the customer package).

The example shown in demonstrates how a customer override is achieved.
In this example the customer pgibsa has the Contact document.xml and edit view overridden within the admin module. Note that only the overridden artefacts are included in the override. All other aspects of the module will respect the generic functionality declared in the module package (rather than the customer package).
Note also that the implementation (Impl) class for Contact is also overridden however this override is generated automatically by Skyve using the generateDomain ant task.
Database persistence of relationships and key constraints
To ensure referential integrity, Skyve (via Hibernate™) persists foreign key constraints in the data tier, as follows:
| Relationship | Description | Logical types |
|---|---|---|
| aggregation association | When an aggregated association is declared from A to B, the database table for document A will have a UUID field created named according to the name declared on the association in document A, suffixed _id. For example, if Invoice has an aggregated association to Employee, typically the name of the association might also be employee (camelCase). If the persistent name of the Invoice document (i.e. the name of the database table) is INV_Invoice, then this table will have a field called employee_id which holds the UUID key for the Employee record.In this example, Invoice.employee would be a reference to Employee.bizId and would be stored in the database as Invoice.employee_id. Hibernate will ensure that a Foreign Key constraint is created on INV_Invoice table to ensure referential integrity and the Employee record will not be able to be deleted until the relationship is nulled or changed or the corresponding Invoice record is deleted. |
Many-to-one |
| composition association | As for aggregation association except with cascade delete. For example, if an Employee is a Contact, then Employee will have a composition association to Contact. If the Employee is deleted, the referred Contact will be deleted automatically (i.e. cascade). |
Many-to-one |
| aggregation collection | When an aggregation collection of document B is declared on document A, a directional joining table is created to express the relationship. The joining table will have two fields: owner_id and element_id with foreign key constraints such that owner_id references document A and element_id references document B (i.e. where Bs are elements of A’s collection).The joining table is named according to the direction of the relationship using the persistent names of both documents. For example, a Depot may have a collection of Taxi. If the persistent names of the documents are TRAN_Depot and TRAN_Taxi, the joining table will be named TRAN_Depot_Taxi and the owner_id will reference TRAN_Depot and the element_id will reference TRAN_Taxi. The joining table is directional because if another relationship is declared from document B to document A (i.e. the other way around) another joining table is created such that the owner is document B and elements are document A. When an element of the collection is deleted or removed, the tuple in the joining table is deleted automatically by Skyve. When the owner of the relationship is deleted, the tuple in the joining table is also deleted automatically. |
Many-to-many |
| composition collection | As for aggregation collection except with cascade delete. For example, if Depot has a collection of Taxi which is of type composition, then deletion of the Depot will result in cascade deletion of the associated Taxis and therefore also the tuples in the joining table will be deleted. |
Many-to-many |
| parent-child collection | When a parent child relationship is declared from A to B, document B will have a parent property (with corresponding .getParent() and .setParent() methods) and the table for document B will have a parent_id field created.For example, if the Invoice document is declared as parent to InvoiceLine and the persistent name of the InvoiceLine document is INV_InvoiceLine then this table will have a column parent_id which holds the UUID key of the parent Invoice. |
One-to-many |
Database indexes
Hibernate ensures that all primary keys are indexed unique and that all tables have a primary key defined.
Skyve platform columns bizCustomer (the customer context in which the data was created), bizKey (the Java String representation of the bean) and bizUserId (the user who created the data) are also indexed.
In addition, developers can declare a database index on document attributes, or turn off the default indexing behaviour where it is not required, as follows:
<longInteger name="millis" required="true">
<displayName>Millis</displayName>
<index>database</index>
</longInteger>
<memo name="auditDetail" required="true">
<displayName>Audit</displayName>
<index>none</index>
</memo>
Java classes
Skyve provides a generateDomain ant task which generates java classes as required for each document. These classes are located in the module domain folder.
For each document a generic document interface class is generated as well as an implementation class (Impl). Bizlet code uses these interfaces so compile errors are generated if developer code is inconsistent with the application specification metadata.
An Impl class is also generated for each customer-override of the document (located in the customer’s module.document override package).
Bean
Each document class extends the Bean interface.
Beans include a number of attributes to support Skyve interactions, specifically:
| Attribute | Description | logical type |
|---|---|---|
| bizId | A guaranteed unique primary identifier for the instance of the bean | UUID (universally unique identifier) |
| bizKey | A simple scalar representation of the bean. | String |
| bizCustomer | The name of the customer/tenant the instance belongs to. | String |
| bizDataGroupId | The id of the datagroup context which the bean instance belongs to. | UUID |
| bizUserId | The id of the user who created the bean. | UUID |
| bizModule | The name of the Skyve module in which the instance exists. | String |
| bizDocument | The name of the Skyve document which this bean is an instance of. | String |
| bizOrdinal | The ordinal position of the bean if it exists as a member of a collection. | Integer |
| persisted | Whether the bean has been persisted. For transient beans this will always return false. | Boolean |
| created | Whether the bean has been validly created. | Boolean |
Bean attributes
Each generated document interface class implements either PersistentBean or TransientBean and represents the intersection of all customer-overrides.
PersistentBean
In addition to the basic attributes required for beans, PersistentBeans contain attributes required for persistence (including attributes to allow record locking and contention management) so that any persistent document created within Skyve has all aspects required for secure multi-user interactions.
| Attribute | Description | Logical Type |
|---|---|---|
| bizLock | Platform and database independent optimistic locking information consisting of a timestamp and username. Comparing lock values allows the platform not only to determine IF the bean has been altered by another conversation since it was loaded into the current conversation, but also by WHOM and WHEN. |
OptimisticLock |
| bizVersion | An incrementing integer that is used to detect if changes have been made by another conversation. | Integer |
| bizFlagComment | Users can add to comments the document instance as part of generic list functionality called Flags. | String |
| bizTagged | Indicates whether a bean is a part of the currently selected tag within the context of the conversation. While relevant for persistent beans, the value of bizTagged is not itself persisted. | Boolean |
PersistentBean attributes
Persistence and locking
Persistent Skyve documents are persisted as tables in the data tier, and document instances as data rows or tuples. Document attributes containing content (i.e. file attachments) contain only a reference to the actual content (which is managed within the file system).
Skyve tables always have columns for the Bean and PersistentBean attributes defined above, in addition to those defined by the developer in the document.xml. This guarantees that every table can automatically be managed by Skyve in a secure, scalable and transactional way.
While some DBMS implement their own proprietary contention and record locking mechanisms, Skyve implements these in a platform and database-independent way.
Pessimistic locking happens in the data tier (page, row, table DB locks) - these are for each database connection and handled by the DBMS.
Optimistic locking happens during user wait time (also called long transactions) and relies on a piece of data which changes each time someone changes a tuple. Optimistic locking is required because holding database connections open while users interact with the system would severely impact on performance and infrastructure requirements for multi-user systems.
Next Converter, validator and format
Previous Modules