Maven targets
Maven targets
Specific to the Java implementation of Skyve, Skyve projects a number of Maven target utilities to assist developers. The Maven targets provided can be customised where required.
The maven targets are located in your project config/ folder. To run the target, right click the target and choose Run As.

Once the target has been run, it will be available in the Run menu.

generateDomain
mvn skyve:generateDomain
Generate domain validates and compiles the metadata (XML files) in your project and checks that the application domain is in a valid state. Errors for the developer to fix are written to your console, and if generate is successful, the domain will be compiled to produce Java domain files and unit tests.
generateEditView
mvn skyve:generateEditView
Generate edit view requires to additional parameters, a module and document key value pair.
If no edit.xml is declared for a document, Skyve will create a scaffolded view automatically using the attributes specified in the document. When customising a view, it is useful to start from that scaffolded view and extend it.
The target will prompt for the customer, module and document parameters. If no document is specified, the target will generate edit views for all documents within the module.

This target will write a file within the views package of the module and document specified by the parameters called generatedEdit.xml . Once created, rename this file to edit.xml (or, if using this file as a view component, the name of the component).
generateDefaultQueries
mvn skyve:generateDefaultQueries
Similar to having a scaffolded edit view for new documents, when documents are shown in a list from a menu or in a lookupDescription, the /default query/ will be used which defines which columns are shown. This maven command can write out all the default queries to a file in the project root so any queries can be tweaked and included in your module.xml.
The target will prompt for customer and module.
Skyve Script
mvn skyve:script
This will look for a file called skyve.md inside a script directory in your project root. Any modules and documents found inside this file will be generated and added to your project. For more user feedback, this can also be performed via the UI from admin -> Document Creator.
Update resources
mvn clean compile war:exploded
Depending on how you configure your Wildfly, if you are not publishing changes during development into wildfly/standalone/deployments, you can use this maven command to update your local /deployments/ directory with the compiled project. Your Wildfly deployment scanner can then be set to watch this location.
Local deploy
man compile war:exploded skyve:touch
This refreshes your projects /deployments directory and creates a projectName.war.dodeploy file telling Wildfly to restart the module. This is used when there are any Java or module changes which are cannot be hot-reloaded.
Updating the Skyve version
To update your project with a specific Skyve version, you’ll need to pull/check-out the Skyve project (from https://github.com/skyvers/skyve.git) prior to the following steps, ensuring you pull the specific Skyve version you’re after. If in doubt, pull Skyve and check which version is retrieved. Releases are tagged, so it is typically safest to checkout the last tagged commit.
Warning: before continuing, make sure your project is under source control, and all files are committed locally. Upgrading a project can change lots of files, and will update your admin module and web resources. Any local changes you have made will be overwritten and need to be merged back in manually.
Configuring the assemble target
These instructions apply to projects created using the Skyve project creator. If you created your project manually, these steps may differ.
- If using Eclipse, create a new Run Configuration target, setting the base directory to your project’s workspace, and setting the goal to
skyve:assemble. Once setup in your pom this can also be run from the command line withmvn skyve:assemble. - In your project’s
pom.xml, update the skyve.version property to match the version of Skyve you pulled/checked out- Find the Skyve plugin (search for artifactId
skyve-maven-plugin) and configure the<skyveDir></skyveDir>setting with a relative or absolute path to the Skyve project local drive location (where you pulled to) - Set your
<customer></customer>to match the customer in your project - Save your
pom.xml
- Find the Skyve plugin (search for artifactId
- Run the assemble target you have just created, resolving any reported issues
- When successful, run your project’s generate domain target, resolving any reported issues
- When successful, run your project’s unit tests, checking the upgrade did not interfere with any expected behaviour
- When successful, run your project’s generated tests
- Deploy your project locally and sanity check everything still works correctly
- When satisified, commit the changes to your project
Javadoc
Skyve provides a javadoc target which generates a documentation set incorporating:
- doc metadata attributes as specified in the Skyve metadata,
- generic javadoc, and
- logical model graph, generated using graphviz “dot” application.
To ensure that graphviz can generate model graphs, ensure that ..\Graphviz\bin is in your OS Environment variables path.
Custom javadoc can also be created using the usual doclet interface.
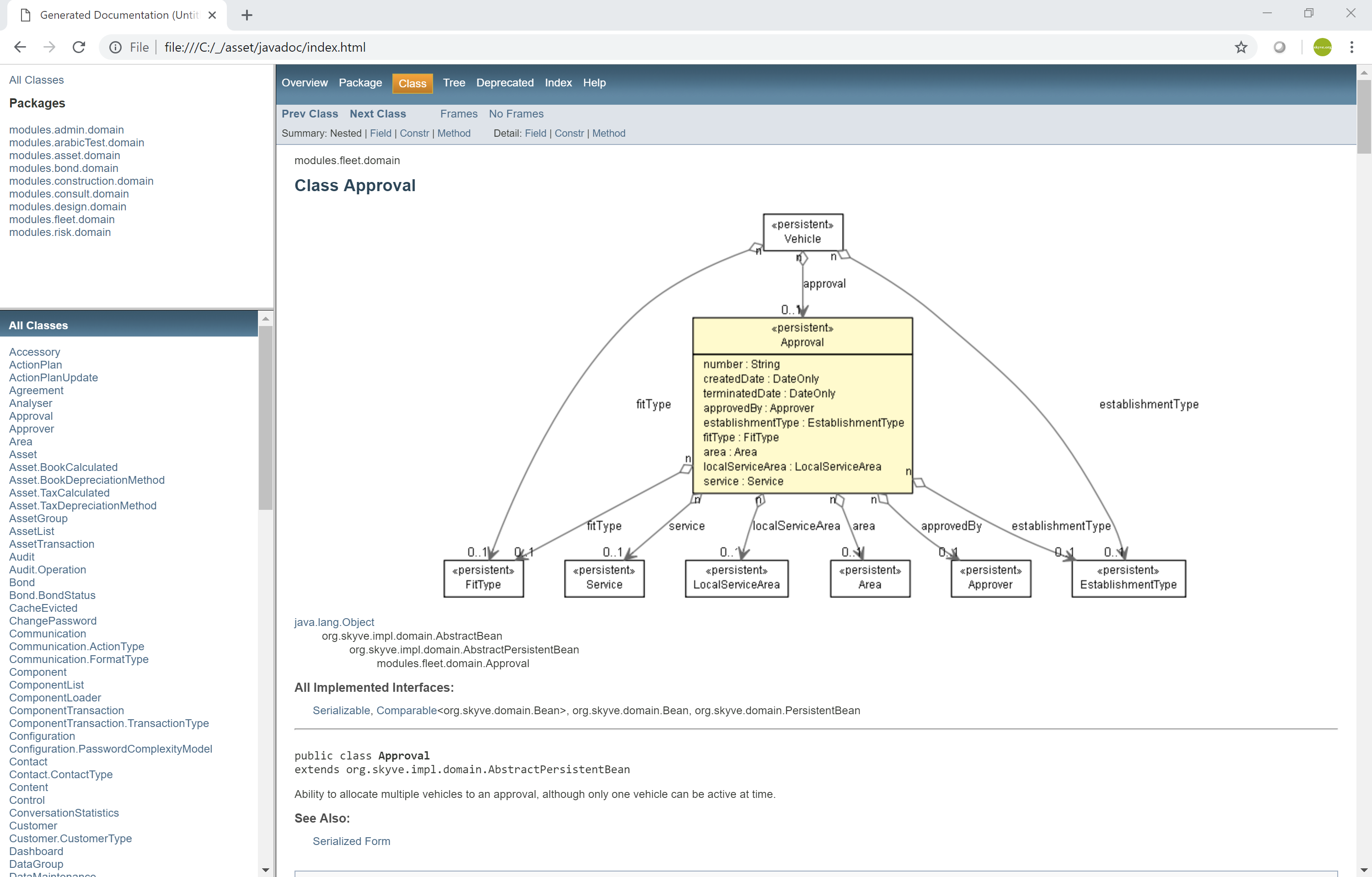
The javadoc utility includes a combination of the application metadata formatted and combined with the embedded documentation.

Example of formatted application specification combining metadata and embedded documentation
Skyve includes documentation attributes at every level of application metadata.
Users can include basic html-style documentation within the metadata
documentation attributes. The utility assembles this html and combines it with
self-describing metadata (like tool-tip definitions already embedded in
the metadata), according to the concepts inherent in the platform.
The utility creates a full documentation set including:
- Titles,
- Overviews,
- Indexes and Table of Contents for each section,
- Automatic numbered references for each section, table and figure,
- Internal links, and
- External links.
Because the utility generates documentation for every part of the application specification, it encourages developers and technical writers to be thorough and cover all aspects of the application they are documenting.
Graphviz Install
- Navigate to
https://www.graphviz.org/download/ - Find the install package that suits your system requirements and click on the link
- Choose your method of install (this guide will cover installation for Windows OS from a .msi file) and click the link
- The download will start, once downloaded, navigate to where the file downloaded and double click the file
- The Graphviz installer will open, click
Nextto follow onto the next page - Designate your Installation folder and click
Next, then again clickNextto start your install - Once Graphviz has completed installing, click
Closeto exit the wizard
Next Content Repository Tools
Previous Lists